How does the Taliban’s foreign policy in 2025 balance ideology, survival, and diplomacy? Explore Afghanistan’s ties with Pakistan, China, Iran, and global powers, and its quest for legitimacy and stability.
Introduction: What Defines Taliban Foreign Policy Today?
Since the Taliban’s return to power in August 2021, Afghanistan’s foreign policy has followed a cautious yet pragmatic path. Unlike conventional states, the Taliban must balance ideological commitments with pressing needs such as economic survival, security, and international recognition.
Their approach combines pragmatism, regional balancing, and selective engagement with global powers. Understanding this strategy is key to assessing Afghanistan’s role in the evolving multipolar world.
Read more on South Asia News
How Does the Taliban Engage with Neighboring Countries?
Regional diplomacy forms the backbone of Taliban foreign policy. Afghanistan’s neighbors are both partners and strategic constraints.
Latest Post
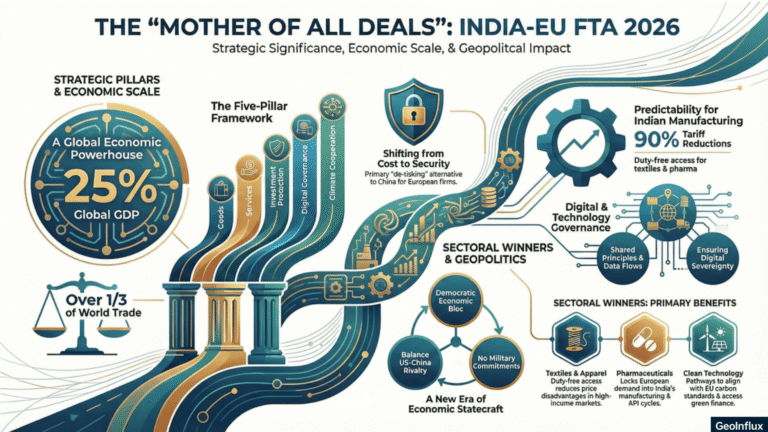
India-EU Free Trade Agreement 2026 Explained: Why the “Mother of All Deals” Is Reshaping Global Trade and Power
- Pakistan: Islamabad remains the Taliban’s most influential partner. Pakistan provides political support, security guidance, and economic assistance. It also helps the Taliban manage internal factions and maintain domestic stability. Tensions remain over cross-border militancy, as Afghanistan navigates its relationship with India.
- China: Beijing engages the Taliban primarily on economic and security fronts. Cooperation focuses on counterterrorism and infrastructure development, potentially integrating Afghanistan into the Belt and Road Initiative. China’s engagement allows the Taliban to secure investment without demanding full international recognition.
- Iran: Relations are pragmatic. Tehran is interested in border security, trade, and energy cooperation. Ideological differences, especially concerning Shia communities, require cautious diplomacy.
- Central Asia: Uzbekistan, Turkmenistan, and Tajikistan engage with Kabul for trade and security purposes. These relationships are transactional and focused on immediate regional stability rather than long-term strategic alliances.
How Does the Taliban Approach Global Powers?
The Taliban’s interactions with major global actors are cautious, selective, and survival-driven:

- United States & Western Nations: Engagement is limited and conditional, focusing on human rights and counterterrorism. Dialogue with the West allows the Taliban to negotiate humanitarian aid and sanctions relief without compromising domestic ideological positions.
- Russia: Relations with Moscow are transactional. Afghanistan cooperates on intelligence sharing and counterterrorism, while Russia balances influence in Central Asia and concerns over extremist spillover.
- United Nations & Multilateral Organizations: The Taliban seeks humanitarian engagement to stabilize the economy, yet full diplomatic recognition remains unlikely due to concerns over governance and human rights.
What Are the Taliban Foreign Policy Priorities?
The Taliban Foreign Policy strategy is guided by four main objectives:
- International Legitimacy: Securing formal recognition without major ideological concessions.
- Economic Stability: Ensuring trade, investment, and aid to prevent economic collapse.
- Security and Counterterrorism: Managing internal militant factions while mitigating threats that could provoke international intervention.
- Strategic Balancing: Leveraging relationships with regional powers while avoiding overdependence on any single actor.
How Does Ideology Influence Taliban Diplomacy?
Ideology underpins the Taliban’s governance and subtly shapes foreign policy:
- Sharia-Based Policies: Enforcement affects women’s education and public participation, limiting engagement with Western nations.
- Islamist Affinity: Ideological alignment with regional Islamist movements guides informal alliances, even as it complicates global recognition.
- Selective Pragmatism: The Taliban engages pragmatically where survival and legitimacy are at stake while maintaining ideological credibility at home.
What Are the Strategic Implications for the Region?
The Taliban foreign policy affects South Asia and the wider geopolitical landscape:
- Regional Security: Pakistan gains influence, while India recalibrates its Afghanistan strategy.
- Counterterrorism: Cooperation against ISIS-K and Al Qaeda is critical but uncertain.
- Economic Connectivity: Engagement with China and Central Asia could enhance Afghanistan’s trade integration, though sanctions and infrastructure gaps remain barriers.
- Diplomatic Isolation vs. Engagement: Afghanistan’s ability to navigate sanctions, attract investment, and maintain internal control will determine the Taliban’s long-term survival.
What Challenges Does the Taliban Face in Diplomacy?
- International Recognition: Western countries remain hesitant due to human rights concerns.
- Economic Collapse: Reliance on foreign aid and informal trade routes exposes Afghanistan to vulnerabilities.
- Factionalism: Internal Taliban divisions complicate consistent foreign policy.
- Regional Rivalries: Balancing relations with Pakistan, China, Iran, and Central Asian states requires constant negotiation.
Strategic Insights: How Will the Taliban Shape Afghanistan’s Global Role?
The Taliban foreign policy reflects a pragmatic balance between ideology and survival:
- Maintaining regional partnerships while avoiding overreliance on any single country is crucial.
- Engaging selectively with global powers may ease sanctions and secure humanitarian aid.
- Managing internal security and counterterrorism commitments is key to maintaining international credibility.
- Long-term economic stabilization depends on infrastructure investment and trade integration with China and Central Asia.
Recap Table: Key Questions About Taliban Foreign Policy
| Question | Answer Summary |
|---|---|
| Who are the Taliban’s main regional partners? | Pakistan, China, Iran, and Central Asian states (Uzbekistan, Turkmenistan, Tajikistan). |
| How does ideology affect diplomacy? | Sharia law and Islamist affiliations shape engagement with Western nations and regional groups. |
| What are Taliban foreign policy priorities? | Legitimacy, economic stability, security, strategic balancing. |
| How do global powers engage with the Taliban? | Selectively, focusing on aid, counterterrorism, and humanitarian cooperation. |
| What challenges does the Taliban face? | Recognition, economic vulnerability, internal factionalism, regional rivalries. |
Conclusion: What Does the Future Hold for Taliban Foreign Policy?
The Taliban foreign policy in 2025 is a cautious blend of pragmatism and ideology. Survival, legitimacy, and economic stability guide their regional and global engagement, while ideological constraints limit acceptance by Western powers. Success will depend on balancing regional alliances, attracting investment, managing internal security, and selectively engaging with global actors. Afghanistan’s trajectory under the Taliban will continue to influence South Asian security and global geopolitical calculations.
References: What Are the Sources of This Analysis?
- BBC News – Taliban: Afghanistan’s New Foreign Policy Challenges
- Al Jazeera – Taliban Diplomacy: Balancing Regional Ties
- The Diplomat – Taliban’s Relations with China and Central Asia
- Carnegie Endowment – Afghanistan in a Multipolar World
- Council on Foreign Relations – Taliban Governance and International Recognition





Pingback: Why India Firmly Says No To US Bagram Air Base Afghanistan: 5 Geopolitical Shocks | GeoInflux GeoInflux
Pingback: Pakistan Air Strikes Afghan Cricketers: 3 Dead In Paktika, Afghanistan Historic Boycott | Geoinflux Analysis GeoInflux
Thanks for sharing excellent informations. Your website is so cool. I am impressed by the details that you have on this site. It reveals how nicely you understand this subject. Bookmarked this web page, will come back for extra articles. You, my pal, ROCK! I found simply the information I already searched all over the place and just couldn’t come across. What a great web site.